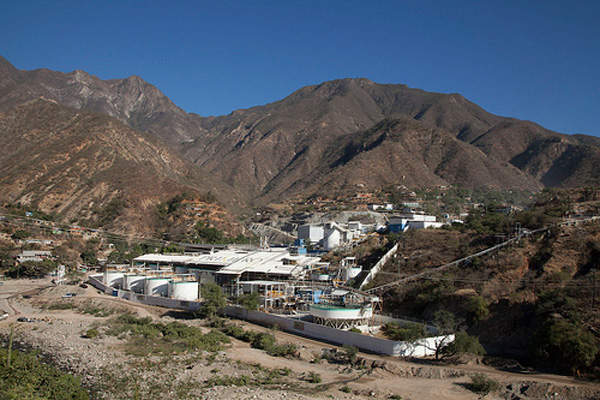
The San Dimas gold-silver mine in Durango, Mexico, is owned by Primero Mining. The low-cost gold and silver mine located in the central part of the Sierra Madre Occidental mountain range has been operating for more than 100 years.
The mine produced 111,983oz of gold and 6.05 million ounces (Moz) of silver in 2013. It is currently undergoing an expansion programme to increase the mill capacity from the existing 2,500t per day (tpd) to 3,000tpd, which will result in annual average production of approximately 215,000 gold equivalent ounces.
Construction for the expansion project is anticipated to commence in 2015 and complete in the second quarter of 2016.
Mine location and background
Related content
La Parrilla Silver Mine, Mexico
La Parrilla silver mine is located in the state of Durango in Mexico and the underground mine produced 1.5Moz of silver in 2010.
The San Dimas gold-silver deposit is located in a mountainous region of the San Dimas district, approximately 125km north-east of Mazatlan in central-west Mexico, at an elevation ranging from 2,400m on the high peaks to 400m in the valley of the Piaxtla River.
Primero Mining acquired the San Dimas mine in 2010 from Goldcorp. The mine’s historical production at the time of acquisition stood at 11Moz of gold and 582Moz of silver.
The San Dimas deposit comprises five ore zones or blocks: San Antonio West, Sinaloa Graben, Central Block, Tayoltita and Arana Hanging Wall block. Tayoltita is the oldest operating mine in San Dimas and is accessed via a 4.4km tunnel from a portal.
San Dimas mine geology and reserves
The San Dimas mine region consists of two major volcanic successions: the lower volcanic group (LVG) and the upper volcanic group (UVG). The UVG is further divided into a subordinate lower unit and an upper unit called the Capping Rhyolite. The lower unit is made up of lavas of intermediate composition, while the Capping Rhyolite comprises of rhyolitic ash flows and air-fall tuffs.
San Dimas is an epithermal vein-type gold-silver deposit with mineral veining occurring in three major stages in the east-west trending fractures.
As of December 2013, the gold-silver mine was estimated to contain 4.89 million tonnes (Mt) of proven and probable reserves containing 49.48Moz of silver and 870,000oz of gold.
Details of the underground mine expansion
The first phase of the San Dimas mine expansion was completed the first quarter of the year, increasing the mill capacity from 1,500tpd to 2,500tpd.
Primero Mining secured approval for the second phase of expansion in August, to further increase the milling capacity by 500tpd.
This second phase will see the construction of internal tunnels for connecting the central block area and the main mining area at San Dimas, which includes the high-grade Sinaloa Graben mineralisation area.
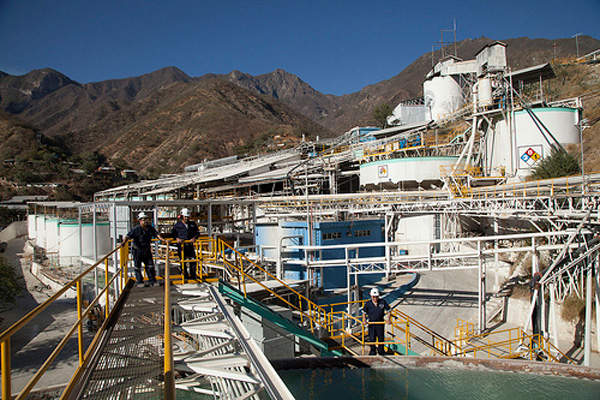
Mining and ore processing at San Dimas
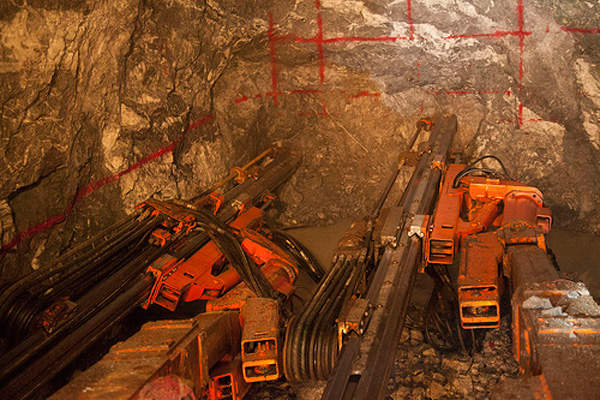
Cut-and-fill mining as well as a long-hole stoping method with drill jumbos or jackleg drills and load-haul-dump machines are employed for the underground mining operations at San Dimas.
The mined ore is loaded and hauled to the surface via dumpers before being sent to the processing plant at Tayoltita mill.
The 2,500tpd Tayoltita mill employs cyanidation and zinc precipitation for gold and silver recovery.
The run-of-mine ore is processed in a two-stage crushing unit and two ball mills prior to leaching. The gold-silver rich solution is separated in a counter current decant (CCD) circuit, after which gold and silver are recovered from the solution in a zinc precipitation circuit. The produced dorè bars are transported to the refineries in the US for further purification.
Tailings are pumped to the tailings impoundment area through a single-stage pumping station.
The silver produced at the mine is sold to Silver Wheaton under a long-term silver off-take agreement. The original offtake agreement was signed between Goldcorp and Silver Wheaton, which was was amended by Primero Mining following the acquisition.
Infrastructure facilities at the gold-silver mine
San Dimas mine is accessed by road from the city of Durango and by air from either Mazatlan or Durango.
The site’s power supply is secured from the Primero-owned hydro-electric power station at Las Truchas, as well as from the state-owned Federal Power Commission Supply System (FPCSS). The mine also uses diesel generators for back-up power.
Water required for the mining operations is sourced from the Piaxtla River.